reCAPTCHA
Background
Bot attacks are rising across e-commerce platforms, leading to fraudulent transactions and significant costs. Although Centra offers post-checkout fraud prevention, early bot detection at the Storefront API level is crucial. To address this, Centra has integrated Captcha, enabling frictionless verification before checkout using tools like Google reCAPTCHA.
How does it work?
Captcha verification consists of two parts: a script evaluated on the frontend, and a backend call to the provider, checking the result. The frontend side if often associated with a visual challenge, where you have to prove that you’re a human, but it doesn’t need to contain any direct user interaction. Google reCAPTCHA v3 does all the evaluation by itself in the background, without showing any challenge at all. Even the previous reCAPTCHA v2 has an invisible mode, with auto-evaluation based on available data points.
It’s worth noting that the list of features and behaviors, which can help discriminate between bots and real users is very big. Browser features like viewport size, installed plugins, fonts, languages, mouse movement tracking, etc. can provide enough information to confidently separate humans from bots. If there’s still not enough confidence, a challenge may be presented. This seems to be the general direction here: less user interaction traded for more data collected and processed.
These collected data points are then encoded into a string, and passed to the backend for evaluation on the side of captcha provider.
Setup
Captcha plugin setup
The plugin setup is very minimal, just select the captcha type and paste the secrets. To obtain them, you must first have a Google Cloud account and create a project in the admin console. Click here to learn more in Google's docs.
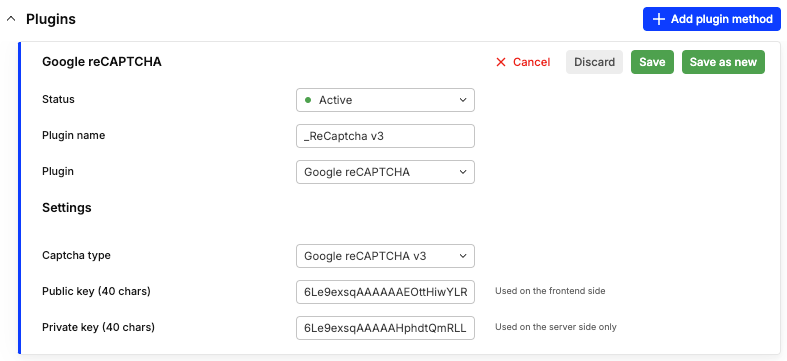
Once it is correctly set up, a new captcha section is added to Storefront API selection responses.
{
"data": { ... }
"extensions": {
"captcha": {
"type": "reCAPTCHA_v3",
"key": "[public site key]",
"script": "<script src=\"https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js?onload=...</script>",
"verified": false
},
"token": "91432ea5-4ddc-cb68-98ad-aa423e9405d6",
"traceId": "2c77d4eb34f9a5d7c022b7f35f6533b7"
}
}
The frontend is then expected to evaluate the contents of captcha.script, which contains a callback to a new mutation verifyCaptcha. When that's successful, the captcha.verified is true, and the script is no longer attached to follow-up responses.
Storefront API plugin setup
After configuring the reCAPTCHA plugin, you should now check the configuration of your Storefront API plugin to find the Captcha section there:

It allows for enabling selective protection of specific endpoints, which need to be secured from bot traffic. Importantly, protection will be enabled as soon as you save the API plugin, so please remember to first implement captcha plugin and verification in your webshop, and only then enable protection of those API endpoints.
Validation flow
The captcha object contains several fields that instruct the frontend how to proceed with captcha verification:
type: Specifies the type of captcha being used. In the example above, it'sreCAPTCHA_v3, which provides frictionless, score-based captcha verification.key: This is the public site key associated with the reCAPTCHA instance.script: This contains the HTML<script>tags needed to load the captcha providers JavaScript on the client side. The script is necessary for executing the captcha challenge, and contains a callback to theverifyCaptchamutation.verified: This boolean flag indicates whether the captcha verification has been successfully completed. Iffalse, it means the client must display the captcha and send the response token back to the server.
The captcha.script contains two <script> tags. The first one is including the captcha code from the provider (it has async + defer attributes), and the other defines a callback that instantly calls the captcha logic, and then sends the result to the verifyCaptcha mutation. This mutation accepts three parameters grouped into a captchaData JSON string:
captchaToken- the result of captcha logic execution,identifier- current Storefront API sessiontoken,pluginId- optional if there is only one active captcha plugin, but still recommended to include.
Centra then sends the captchaToken to the provider’s validation endpoint, which returns a validation status. The verifyCaptcha finally responds with verified being either true or false, but also stores the result in user’s session. It is then reflected in the next selection responses.
The captcha script triggers a custom event centra_captcha_result when it gets the response. You can listen to it like this:
document.addEventListener('centra_captcha_result', handler);
Next, when a captcha-protected endpoint is reached, the stored verification result is checked before any other logic is executed. Missing or failed validation causes a 401 Unauthorized response with captcha: required error, and the same captcha section with the script to execute.
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "captcha error: captcha required",
"path": ["paymentInstructions"]
}
],
"data": null,
"extensions": {
"captcha": {
"type": "reCAPTCHA_v3",
"key": "6Le...mADF",
"script": "\u003cscript src=\"https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js...",
"verified": false
},
"token": "8f39147c-...-9fb01e74b854",
"traceId": "cce7cb7dccd79d56da36ebf884b3d285"
}
}
Frontend side
Captcha scripts can be executed right away, when they are seen in the response for the first time. But that’s just one possibility, the execution may be postponed to some later stage in order to avoid evaluating it for users, which would never reach the checkout. That’s why the captcha section contains all params necessary for the execution: captcha type, plugin ID, and the public (site) key. The captcha script can be executed at any time, and as soon as Centra receives a call to the verifyCaptcha mutation, the session/selection is authorized to access all protected API functions.
It’s crucial that the protection of API endpoints is enabled only after the frontend starts evaluating the captcha scripts, so it will not “just” work. It’s better to double-check the verification flow than accidentally block legitimate users' traffic.
To handle captcha in the front-end, follow these steps:
- Inject the captcha script provided in the
captcha.scriptfield. The execution will happen immediately. - The callback defined in a script sends the collected data (a.k.a captcha token) for verification.
- The session is now verified, which is visible as
verified: truein thecaptchasection. Alternatively, you can include the provider’s script and complete the challenge on your own, using provided details (typeandkey), and then send the result to theverifyCaptchamutation.
async function sendMutationBack(captchaToken) {
const response = await fetch(API_URL, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + SESSION_ID
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query: 'mutation verifyCaptcha($captchaData: String!) {
verifyCaptcha(captchaData: $captchaData) {
verified
userErrors { message, path }
}
}',
variables: {captchaData: captchaToken}
})
});
const body = await response.text();
document.dispatchEvent(
new CustomEvent('centra_captcha_result', {detail: JSON.parse(body)})
);
}
This is exactly what the captcha.script does. Note the custom event centra_captcha_result triggered when the response is fetched. You can listen to it like this:
document.addEventListener("centra_captcha_result", handler);
Q&A
-
What happens when there are more “Invisible Captcha” plugins active at the same time?
- They are both run, and if one of them has a positive verification, it will be selected. So it should be safe to rotate captcha secrets by setting up a new active plugin and then cancelling the old one, always keeping the endpoints protected.
-
What if the captcha plugin gets canceled, but the endpoint protection is still enabled?
- The protection stops working, and there are no 401 responses anymore.
-
Does captcha work with browser extensions blocking external tracking, ads, metrics, etc.?
- Yes, it should still work, captcha isn’t any of the above.
-
Doesn’t captcha negatively affect accessibility to a website, or the user experience in general?
- No, we make the captcha invisible and passive (if possible) so that there is no interaction required at all. Even if the security level is set to very high and a challenge is presented, the captcha provider has one or more solution for alternative verification methods so that it remains accessible to all.